|
Many people either ignore the medicine label or they just do not have the time to sit there and read every word that is written on the box. A medicine box's label tells you what is inside the medicine, how many times you should use it, what the side effects are, how often to use it and more.
All Medicine Labels Include:
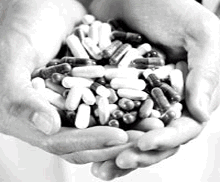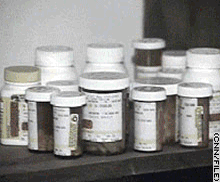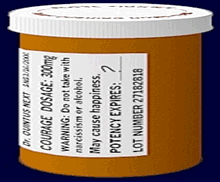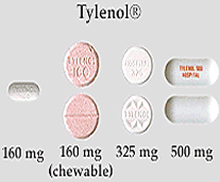
- Active Ingredients: The therapeutic substances in medicine.
- Purpose: The Product Category (examples are: antihistamine, antacid, or cough suppressant)
- Uses: symptoms or diseases the product will treat or prevent.
- Warnings: When not to use the product, when to stop taking the product when to see a doctor, and possible side effects.
- Directions: How much to take, how to take it and how long to take it.
- Other Information: Storage information.
- Inactive Ingredients: Substances such as binders, colors, or flavoring.
When reading a label on a medicine box you should always have enough light because the letters are written so small. It usually takes three times more light to read the same line at age 60 than at age 30. If need be, use your glasses or contact lenses when reading the label. You should always look for statements describing the tamper-evident features before you buy the product and when you use it.
When it comes to medicines, more does not necessarily mean better. You should never misuse over the counter medicines by taking them longer or in higher doses than the label recommends. Symptoms that persist are a clear signal it's time to see a doctor.
Be sure to read the label each time you purchase a product. Just because two or more products are from the same brand family it does not mean they are meant to treat the same conditions or contain the same ingredients.
Some drugs can also interact with foods and beverages as well as with health conditions such as diabetes, kidney disease and high blood pressure. Here are a few drug interaction cautions for some over the counter ingredients:
- Avoid alcohol if you are taking antihistamines, cough-cold products with the ingredient dextromethorphan, or drugs that treat sleeplessness.
- Do not use drugs that treat sleeplessness if you are taking prescription sedatives or tranquilizers.
- Check with your doctor before taking products containing aspirin if you are takinga prescription blood thinner or if you have diabetes or gout.
- Do not use laxatives when you have stomach pain, nausea or vomiting.
Unless directed by a doctor, do not use a nasal decongestant if you are taking a prescription drug for high blood pressure or depression, or if you have heart or thyroid disease, diabetes or prostate problems.
Always check with your doctor before using any type of medication.
Differences Between Brand Name and Generic Medication
What are antibiotics?
How to read medicine labels
Which antibiotics are most frequently used?
HOME
SITE MAP
|